- View Mobile Number
polymer.s@yahoo.com
| Business Type | Manufacturer, Supplier |
| Material | Enteric Coating Material In Pharmaceutical Formulations |
| Type | Pharma Grade |
| Usage | Pharmaceutical Industry |
| Click to view more | |
Product Details
Country of Origin
Made In India
Purity
99%
Form
Powder
Color
White
Brand Name
L-100
CAS No.
25086-15-1
Other Names
METHACRYLIC ACID-METHYL METHACRYLATE COPOLYMER (1:1)
Product Code
25086-15-1
Payment Terms
L/C, D/A, D/P, T/T, Western Union
Delivery Time
3 Days
Packaging Details
20 Kgs and 25 Kgs in Fiber Durm with LDPE liner bag
L 100 are anionic copolymers based on methacrylic acic and methyl methacrylate. Physical properties: It is a solid substance in form of a white powder with a faint characteristic odour. Characteristics: Effective and stable enteric coatings with a fast dissolution in the upper Bowel.
Physiological concepts of the gastrointestinal absorptionThe digestive tube in humans, usually called the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, is a long tube of 10–12 m that begins in the mouth, extend to the anus, and can be divided into the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach, the small intestine and the large intestine. This, along with the salivary glands, liver and pancreas, forms part of the digestive system, whose function is the processing of food and the facilitation of nutrient incorporation to the rest of the body.
The GI tract consists of four
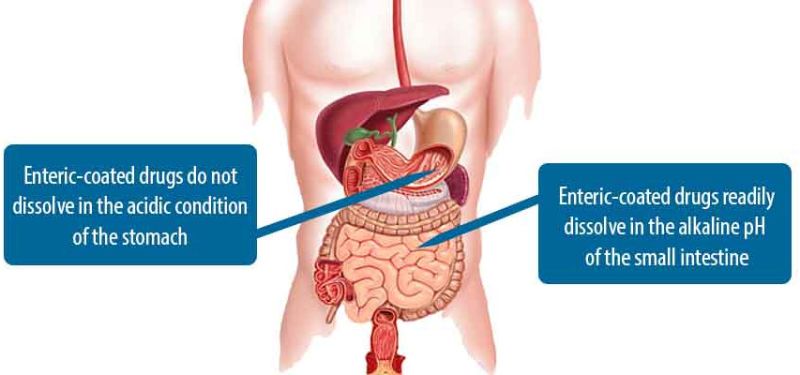
Enteric coating and its function
The enteric coating is an outer coating that can be used in oral pharmaceutical dosage forms, and is usually made up of synthetic polymers or natural products. There are numerous possible motivations for using enteric coating, including altering the odor or taste of the drug adding protection against environmental conditions (especially pH), the protection of gastric mucosa against the irritating action of some drugs or allowing for site or time specific drug release (Shokri and Adibkia, 2013).
The usual polymers used in enteric coatings have carboxylic groups in their composition and their solubility depends on the number of carboxylic groups they contain. Enteric coating polymers may be grouped according to their chemical composition.
Coating process
There are four basic methods for coating solids for the purpose of control drug release: pan coating using solvent evaporation, fluidized-bed coating using solvent evaporation, compaction coating and hot melt coating (Mathiowitz, 1999). In addition to these, other coating methods include microencapsulation, electrostatic coating and 3D printing coating (Wang and Shmeis, 2005).
Looking for "L-100 Methacrylic Acid Copolymer Powder" ?
Kilogram